Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Aspire Tower
Al Aziziyah, Sports City Tower
Building
Completed, 2007
hotel / office
composite
300.0 m / 984 ft
36
137
17
6 m/s
35,000 m² / 376,737 ft²
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Peer Review Engineer traditionally comments on the information produced by another party, and to render second opinions, but not to initiate what the design looks like from the start.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Peer Review Engineer traditionally comments on the information produced by another party, and to render second opinions, but not to initiate what the design looks like from the start.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
The Middle East: 30+ Years of Building Tall
28 November 2018 - CTBUH Research
CTBUH Study Examines Tallest Buildings with Dampers
22 August 2018 - CTBUH Research
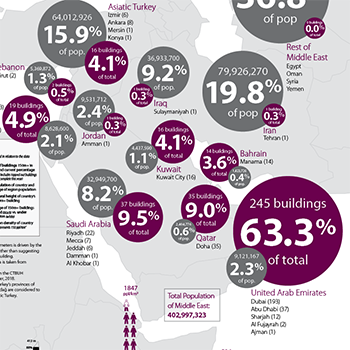
20 October 2018
The Middle East: 30+ Years of Building Tall
CTBUH Research
The Middle East region is hosting its first CTBUH International Conference since 2008. In that year, there were 119 completed buildings of 150 meters or...
The Aspire Tower was built to house the Symbolic Flame of the 2006 Asian Games. The design symbolizes a hand grasping the torch that sits at the tower’s top. The tower houses a five-star hotel, a sports museum, a health club with a cantilevered swimming pool, a revolving restaurant, and an observation deck.
The structural design features a concrete core enveloped in a steel mesh. The cone and lattice shell that house the torch rest atop this structure. The core supports the clusters of floors, which are all cantilevered up to 11.3 meters (37 feet) out from the core. The primary support beams extend radially from the core to steel columns on the outer edge of the structure.
The building features a swimming pool 80 meters (260 feet) above ground that is cantilevered from the core, and extends out 12 meters (39 feet) from the façade. Elliptical in plan, the pool is supported on a substantial steel truss structure some 4 meters (13 feet) deep. The plan geometry of the truss is straight from the core to the column locations, and then elliptical with approximately the same shape as the pool. The truss is connected to the core and supported on two columns that continue down through the levels below, which are supported on vertical trusses.
The façade consists of an energy-efficient glass skin, and helps efficiently maintain comfortable temperature levels in the desert climate.

20 October 2018
The Middle East: 30+ Years of Building Tall
The Middle East region is hosting its first CTBUH International Conference since 2008. In that year, there were 119 completed buildings of 150 meters or...

13 April 2011
Tall and Urban: An Analysis of Global Population and Tall Buildings
Tall buildings are spreading across the globe at an ever-increasing rate. This study demonstrates the relationship between population and tall buildings across those countries and...

31 December 2006
Tallest Buildings Completed in 2006
Nina Tower 1 in Hong Kong, at 319 meters high, leads the list of the ten tallest buildings completed in 2006. The Sports City Tower/Aspire...
28 November 2018
CTBUH has released a Tall Buildings in Numbers (TBIN) interactive data study examining the relationship between high-rise growth and population in the Middle East.
22 August 2018
CTBUH has released a Tall Buildings in Numbers (TBIN) interactive data study on the world's tallest buildings with dampers.
23 April 2014
A regional meeting of the Qatar Chapter was held at the Torch Hotel, located inside the Aspire Tower, and sponsored by Six Construct.
13 April 2011
Tall buildings are spreading across the globe at an ever-increasing rate. This study demonstrates the relationship between population and tall buildings across those countries and presents information on the average height and age of each country’s tallest buildings.
15 October 2009
CTBUH Research & Communications Manager Jan Klerks and Trustee William Maibusch represented the CTBUH as the guests of honor during the TowerTech fair in Doha.
6 March 2008
Though much of the Congress was focused on Dubai, there was the opportunity for delegates to witness the incredible achievements of some of the other cities in the Middle East.
31 December 2006
Nina Tower 1 in Hong Kong, at 319 meters high, leads the list of the ten tallest buildings completed in 2006. The Sports City Tower/Aspire Tower (Doha, United Arab Emirates) at 300 meters, and Eureka Tower (Melbourne, Australia), at 296 meters, were second and third, respectively.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy