Height rank
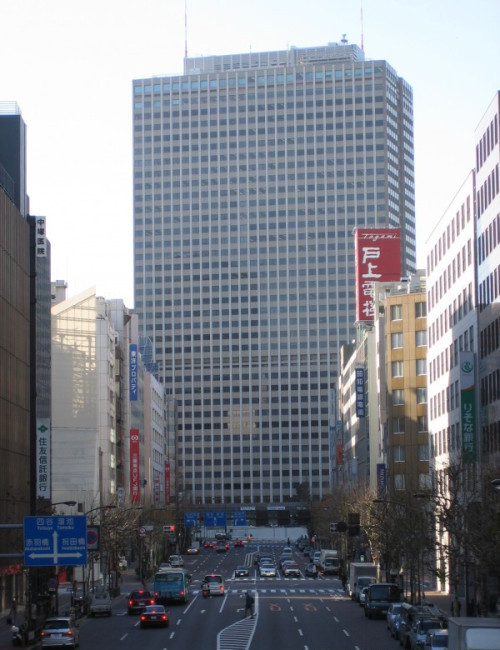
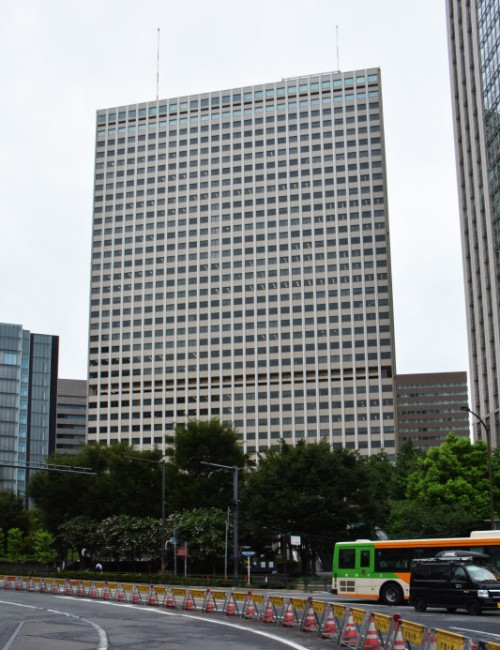
Kasumigaseki Building
Tokyo
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Official Name
Kasumigaseki Building
Other Names
National Education Center
Type
Building
Status
Completed, 1968
Country
City
Address
Postal Code
100-0013
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered a “steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Reinforced Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars.
Precast Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning system are constructed from steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. steel, concrete, timber), one on top of the other. For example, a steel/concrete indicates a steel structural system located on top of a concrete structural system, with the opposite true of concrete/steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used in a composite building’s core, columns, and floor spanning separately.
steel
Height
156.0 m / 512 ft
Floors Above Ground
36
Floors Below Ground
3
Top Elevator Speed
5 m/s
Tower GFA
153,223 m² / 1,649,279 ft²
-
By function
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Start
Completed
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Developer
Mitsui Fudosan Co. Ltd.
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Kajima Design; Yamashita Sekkei
Main Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Kajima Corporation
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Research
20 May 2015
Advanced Structural Technologies For High-Rise Buildings in Japan
Masayoshi Nakai, Takenaka Corporation
This paper reviews the development and current status of seismic design for high-rise buildings in earthquake-prone Japan. Additionally, it briefly describes two important areas of...
Research

20 May 2015
Advanced Structural Technologies For High-Rise Buildings in Japan
This paper reviews the development and current status of seismic design for high-rise buildings in earthquake-prone Japan. Additionally, it briefly describes two important areas of...

10 October 2004
High-rise Reinforced Concrete Building in Japan
This paper surveyed the high-rise RC buildings designed from 1972 till 2001 year about height of a building, structure form, material strength, etc.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy




















