Filter by
Note: As this project is proposed, the data is based on the most reliable information currently available. This data is thus subject to change until the building has completed and all information can be confirmed and ratified by the CTBUH.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Signature Tower Jakarta
The Signature Tower
Building
Proposed
hotel / office
composite
638.0 m / 2,093 ft
113
6
300
3001
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
What Makes Tall, Tall
29 September 2015 - Event
CTBUH Launches Indonesia Chapter
5 July 2013 - Event

17 October 2016 | Jakarta
Mega Size Mixed-Use Projects: Redefining Vertical Urbanism
Monday October 17, 2016. Shenzhen, China. Dennis Poon of Thornton Tomasetti, presents at the 2016 China Conference Session 4c: Structural & Geotechnic Engineering. As the...
20 March 2020
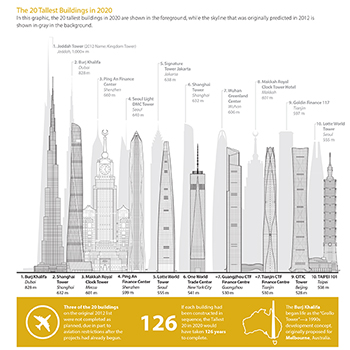
The Tallest 20 in 2020: Predictions vs. Reality
CTBUH Research
In the first edition of the 2012 Journal, CTBUH published a Tall Buildings in Numbers study titled Tallest 20 in 2020: Era of the Megatall—The...

17 October 2016 | Jakarta
Mega Size Mixed-Use Projects: Redefining Vertical Urbanism
Monday October 17, 2016. Shenzhen, China. Dennis Poon of Thornton Tomasetti, presents at the 2016 China Conference Session 4c: Structural & Geotechnic Engineering. As the...

21 September 2012 | Jakarta
Interview: Signature Tower Jakarta
Sugeng Wijanto of PT Gistama Intisemesta and Tiyok Prasetyoadi of PDW Architects are interviewed by Jeff Herzer during the 2012 CTBUH Shanghai Congress at the...
21 September 2012 | Jakarta
The Signature Tower: Reaching High in the Sky of Indonesia
This presentation discusses the reasons behind the selection of the structural systems, as well as the use of advanced structural analyses and design methods, including...

20 March 2020
The Tallest 20 in 2020: Predictions vs. Reality
In the first edition of the 2012 Journal, CTBUH published a Tall Buildings in Numbers study titled Tallest 20 in 2020: Era of the Megatall—The...

20 March 2020
The Tallest 20 in 2020: Then and Now
This research paper undertakes a review of the 2012 report by the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat, “Tallest 20 in 2020: Entering the...

19 September 2012
The Signature Tower: Reaching High in the Sky of Indonesia
This presentation discusses the reasons behind the selection of the structural systems, as well as the use of advanced structural analyses and design methods, including...

18 January 2012
The Tallest 20 in 2020: Entering the Era of the Megatall
Within this decade we will likely witness not only the world’s first kilometer-tall building, but also the completion of a significant number of buildings over...
29 September 2015
CTBUH Atlanta recently hosted an event focusing on the design and construction criteria unique to tall buildings, asking what makes tall, tall?
5 July 2013
At the site of the future Signature Tower a discussion was held on the rapid growth experienced by Indonesia drawing more than 100 participants.
21 September 2012
This presentation discusses the reasons behind the selection of the structural systems, as well as the use of advanced structural analyses and design methods, including Performance-Based Design which considering the risk-targeted MCE levels of seismic hazards. The background of the site, as a part the SCBD super block, is also going to be discussed with the urban design guidelines imposed on it.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy