Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Mercury City Tower
Building
Completed, 2013
123317
residential / office
concrete
338.8 m / 1,112 ft
75
5
137
437
31
7 m/s
173,960 m² / 1,872,490 ft²
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Engineer of Record takes the balance of the engineering effort not executed by the “Design Engineer,” typically responsible for construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Engineer of Record takes the balance of the engineering effort not executed by the “Design Engineer,” typically responsible for construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Top Company Rankings: The World’s 100 Tallest Buildings
13 October 2016 - CTBUH Research
CTBUH Releases Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2014
31 December 2014 - CTBUH Journal
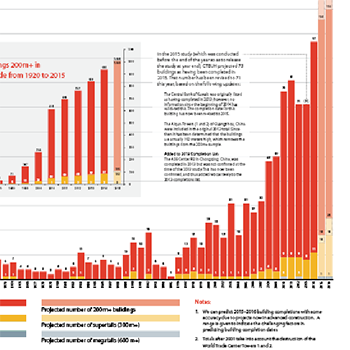
31 December 2014
Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2014
Daniel Safarik, Antony Wood, Marty Carver & Marshall Gerometta, CTBUH
An All-Time Record 97 Buildings of 200 Meters or Higher Completed in 2014 and 2014 showed further shifts towards Asia, and also surprising developments in...
Mercury City Tower is located in Moscow’s bustling International Business Center, a collection of high-rises similar in nature to London’s Canary Wharf and Paris’ La Defense, though it is intended to be much larger in scale. The tower’s distinctive shape allows it to stand out in a busy skyline, but more than its shape, its blazing copper-colored cladding is what makes it unique. The building was originally designed to be surfaced in reflective silver glass in order to mirror the buildings surrounding it, but eventually came to be wrapped in equally reflective bronze-tinted glass. Thanks to its inimitable façade, the tower exhibits a constant glow that makes it appear as though it is continually immersed in the light of the sun on the horizon.
Along with its cladding, Mercury City Tower is memorable for its setback design. The building steps back twice along its northwestern façade, creating a tapering effect that augments the buildings height in tandem with the vertical striping that defines its corners. Each setback has a slanted roof that reinforces the illusion of added height. Though the tower is visually distinct, its façade lacks unnecessary adornments. Rather, the structure and its cladding act together to create a purposeful, clean design. In this way, the building falls squarely into the Structural Expressionist style of architecture.
Located along the topmost floors, the building’s apartments are designed with the flexibility to merge units together, adding to the tower’s overall space efficiency. The building also features a smart “energy cycle” system that regulates energy usage, ambient temperatures, and hot water distribution throughout the development. Although the design of Mercury City is in no way traditional, the typical three-part massing of the volume, comprising a base, core, and crown, imparts the Russian imperatives of strength, reliability, and stability.

31 December 2014
Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2014
An All-Time Record 97 Buildings of 200 Meters or Higher Completed in 2014 and 2014 showed further shifts towards Asia, and also surprising developments in...
JWMarriottMarquisHotelDubai.jpg)
31 December 2013
Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2013
By all appearances, the small increase in the total number of tall-building completions from 2012 into 2013 is indicative of a return to the prevalent...
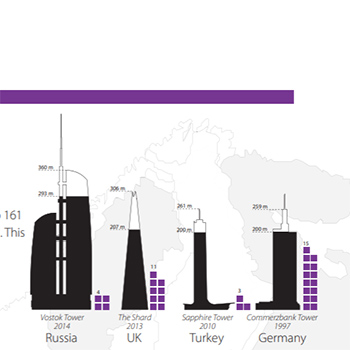
01 June 2013
The Past, Present and Future of the European Skyscraper
There are currently 109 skyscrapers over 150 meters in Europe. This number is set to jump to 161 by the end of 2015, meaning that...
13 October 2016
The Council is pleased to announce the Top Company Rankings for numerous disciplines as derived from the list of projects appearing in 100 of the World’s Tallest Buildings.
31 December 2014
An All-Time Record 97 Buildings of 200 Meters or Higher Completed in 2014 and 2014 showed further shifts towards Asia, and also surprising developments in building functions and structural materials.
31 December 2013
By all appearances, the small increase in the total number of tall-building completions from 2012 into 2013 is indicative of a return to the prevalent trend of increasing completions each year over the past decade.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy